Gait
How we walk changes based on where we are, how fast, how far we are going, and so much more. Gait is the way we describe walking patterns in more detail by looking at things like distance/time between steps or leg position. Since walking is a repetitive motion we can break gait down into a cycle that repeats. We can observe the gait cycle using videos, position-tracking systems, or simply using our eyes.
Since everyone walks a little differently, by analyzing each person’s gait pattern, it allows these differences to be identified. If someone is having difficulties with the way they walk, these gait differences can be used to determine the route of difficulties and possible interventions.
What is involved in a 3D Gait Assessment?
Your gait assessment will include some or, all, of the following components:
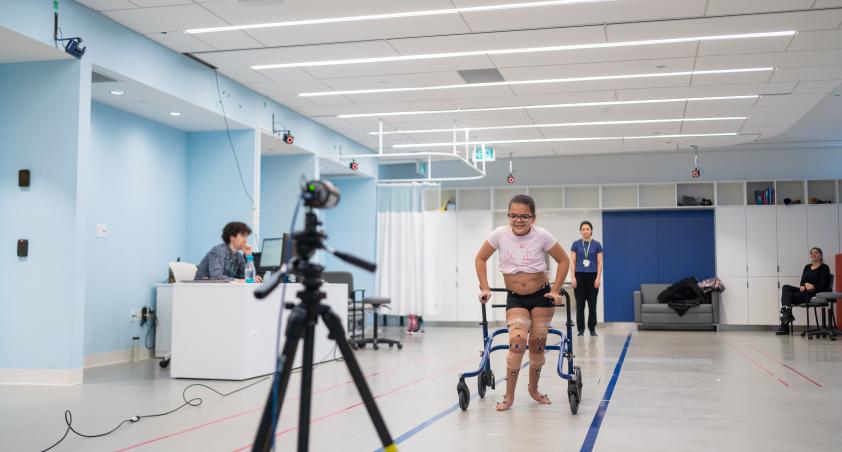
Overview - Two cameras will record you walking from the side and the front. This provides two view points to understand walking patterns. These videos are used in combination with the 3D motion capture cameras, as those cameras can only see the markers and these videos see what is happening before our eyes.
What happens during the assessment? The two cameras record at the same time to capture high-speed videos of the walking patterns.

What happens after the assessment? The videos are synchronized so a single step from the front and side can be analyzed. Videos from different variations of the gait assessment are compared.
Overview - By applying reflective markers on various parts of your legs, the motion capture cameras will take a recording of the markers and create a walking avatar. This will allow us to measure when and how the joints in your body are moving when you are walking.
What happens during the assessment? Reflective markers are placed on various parts on the legs to create the walking avatar.
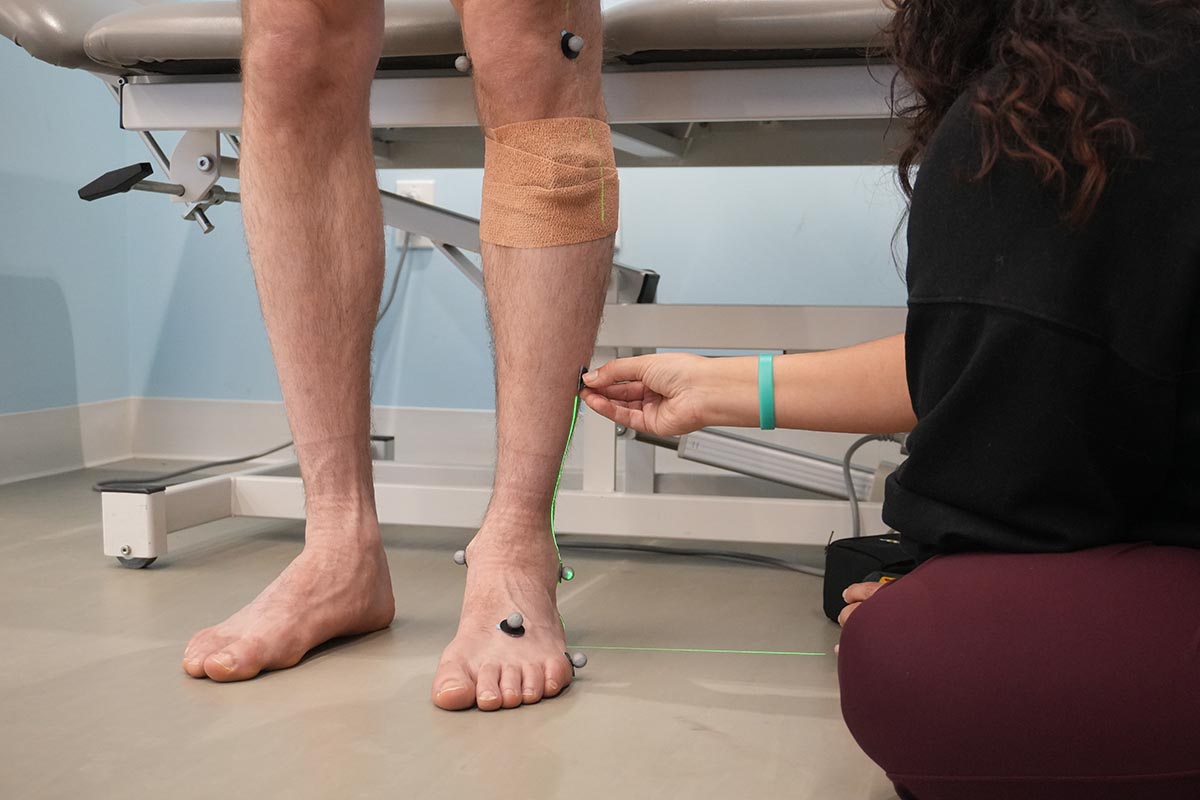
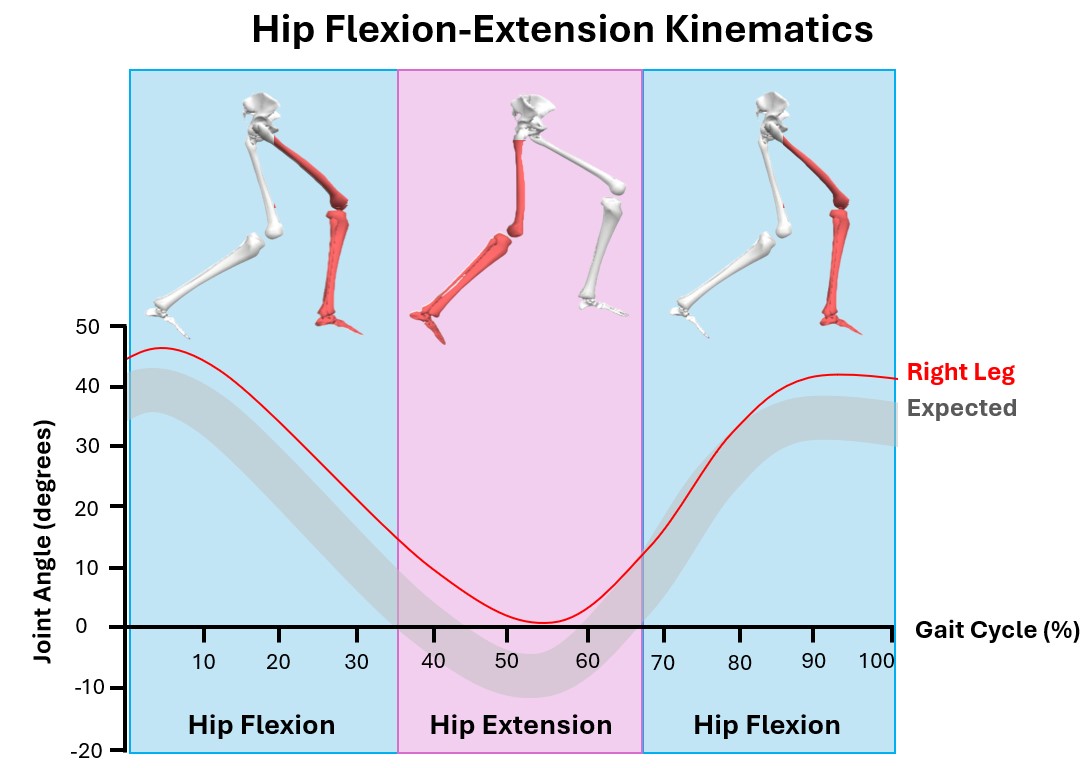
What happens after the assessment? The angles of the joints are calculated to find out the unique details about the way someone walks.
Overview - Force plates in the floor can measure how much pressure you are putting into the ground with your foot. We can then analyze the power produced at the ankle, knee and hip.
What happens during the assessment? Sensors in the floor will measure the force when pushing off, or landing, on the ground.
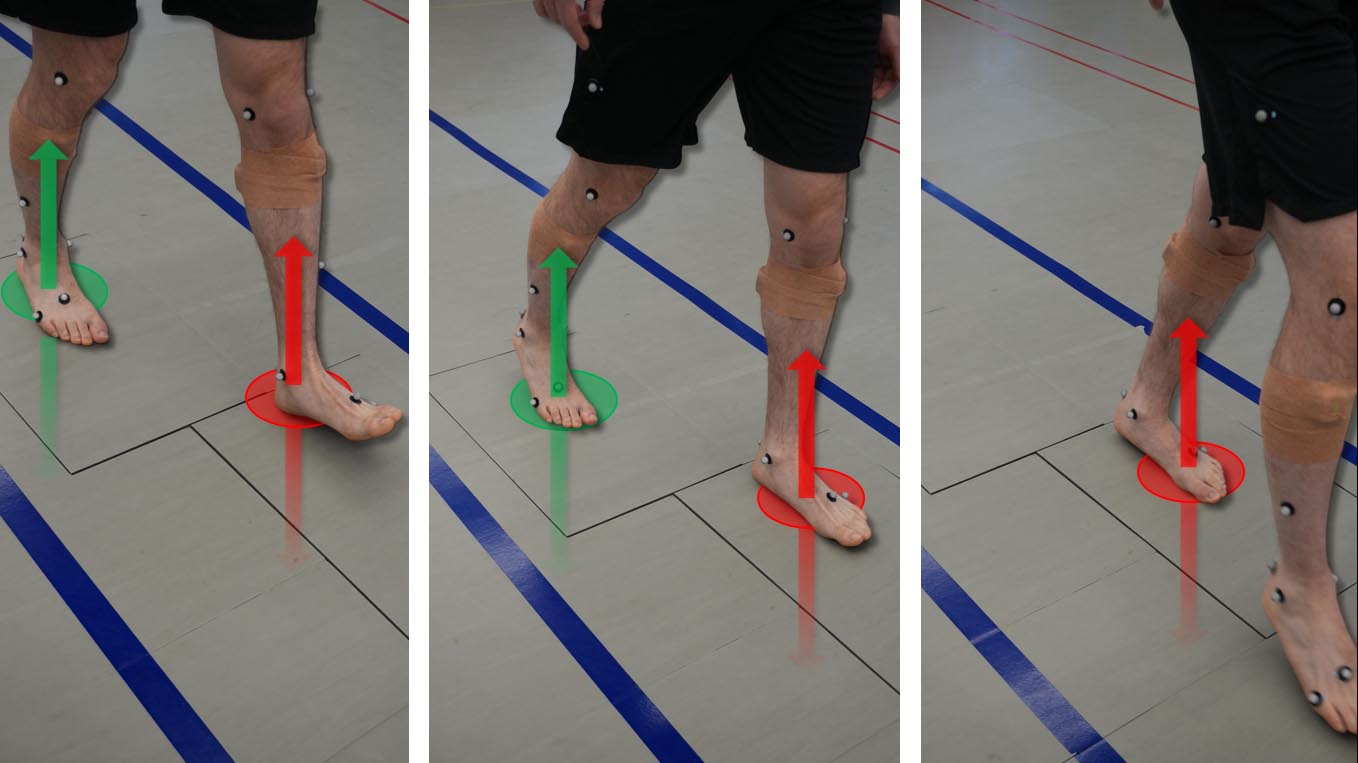
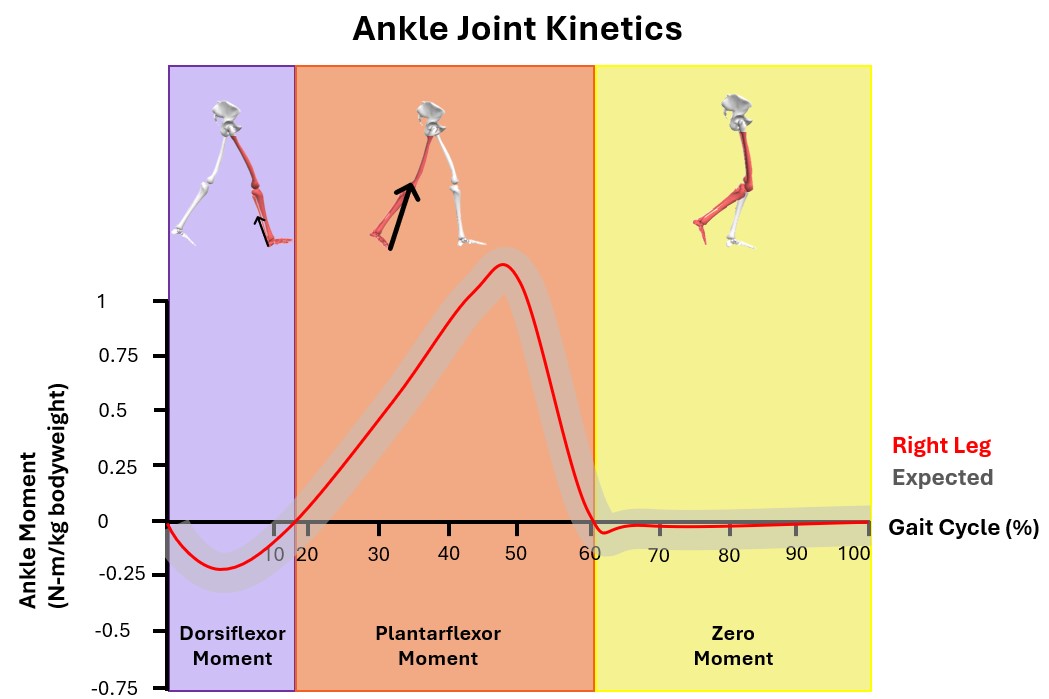
What happens after the assessment? The forces on the joints are calculated using the force from pushing into the floor and based on the angles of the joints, to find out the unique details about the stress on the joints as someone walks.
Overview - By attaching electrodes on the skin using stickers over the muscles in your leg we can learn about when. and how much, your muscles are working when walking.
What happens during the assessment? The muscle-activity sensors are attached to specific muscles.
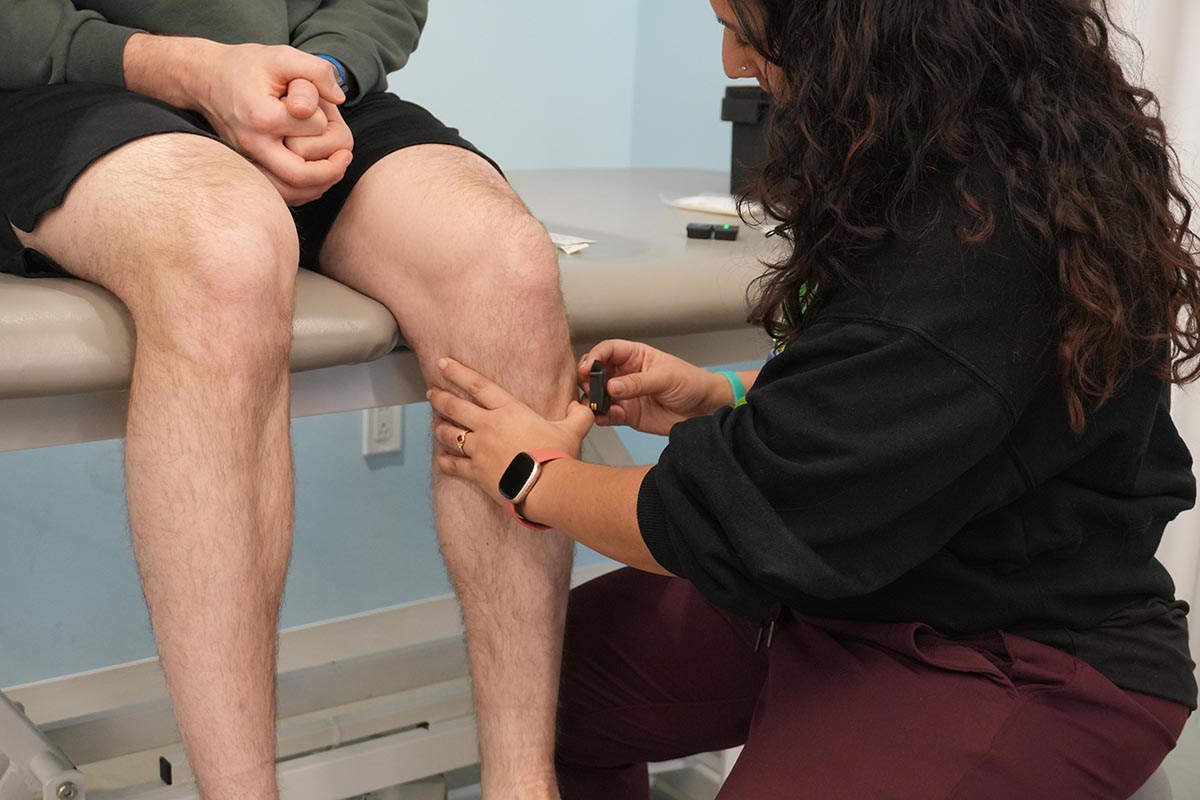
What happens after the assessment? How, and when, the muscles are active is calculated to find out the impact of muscle-activation patterns on how someone walks.
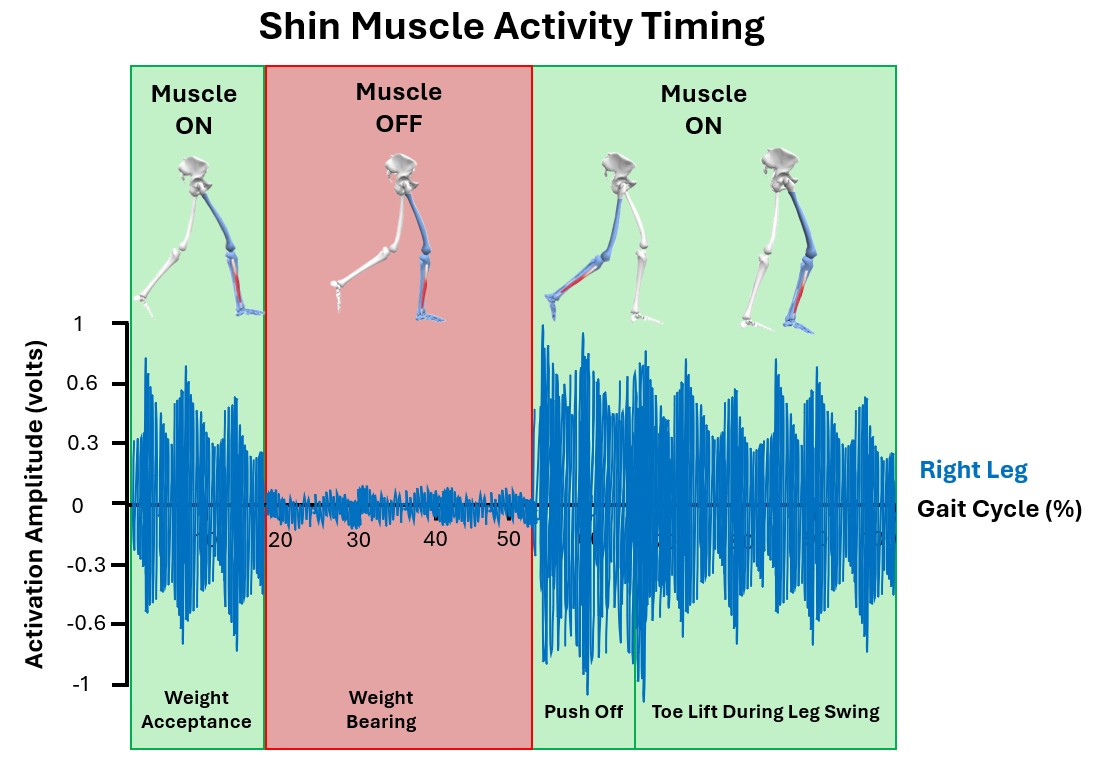
A physiotherapist may perform some, or all, of these physical assessments:
- Range of motion: How much the joints in your legs move
- Muscle strength: How strong the muscles in your legs are
- Gross Motor Function Measure (GMFM): Various activities that look at the way you move, your balance and how you perform different daily activities
- Six-minute walk test: Measures how far you can walk in six minutes
You or your parent(s)/guardian may be asked to fill out questionnaires to let us know more about how you move at home, at school and in the community. This will also tell us how important various movements are in your life. These may include:
- Functional activity questionnaire
- Gait outcomes assessment list
- Pain Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS)
The Motion Analysis Centre technology specialist will work with the computers to create videos of how you move and graphs that quantify when, and how much, you are using various joints and muscles while walking. The physiotherapist will analyze these results and share them with your medical team.
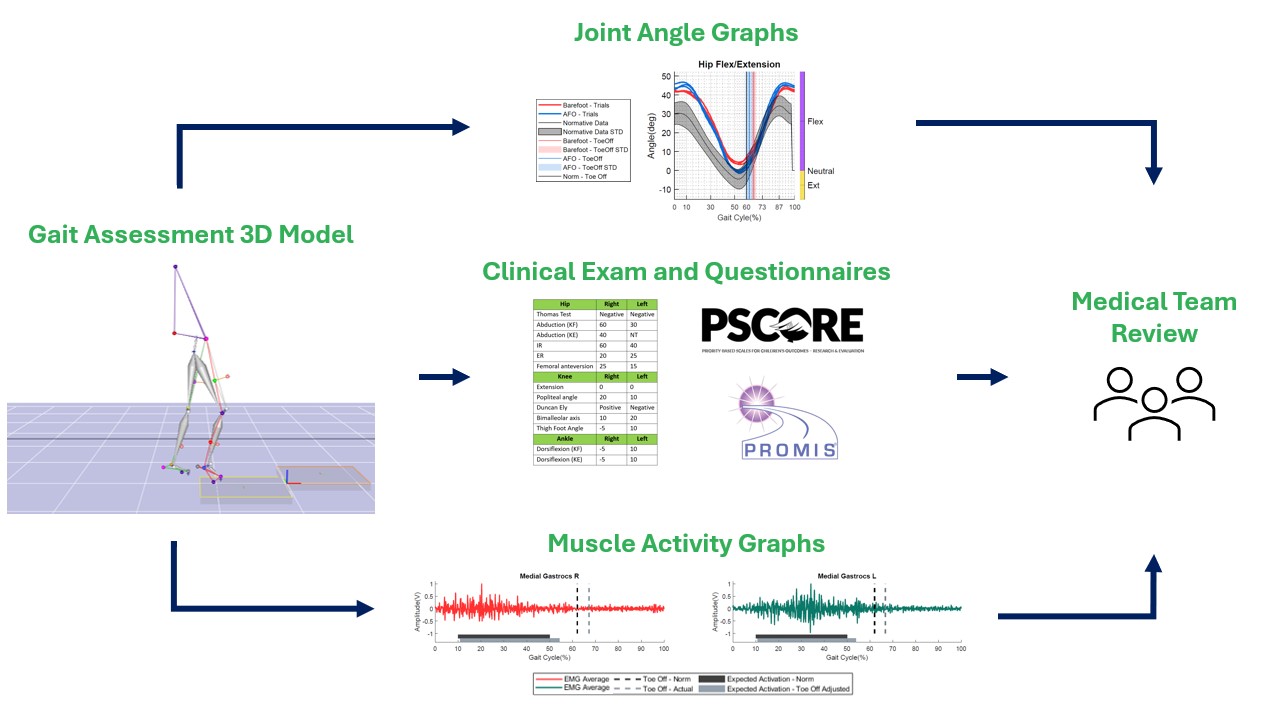
Together with your medical history, physical assessment and questionnaires, the 3D gait assessment will give the team a good understanding of how you move and what the best option is to improve the way you move.
Why 3D Gait Analysis?
The short answer, walking is complex.
The longer answer. The hip, knee, and ankle joints all move at the same time and in multiple directions. So, to get more information about gait we need to be able to track the legs and feet in all directions (up/down, forward/backward, left/right). Therefore, we use 3D motion capture systems to record walking to provide an added level of accuracy over a simple 2D video or observing with our own eyes.
Additionally, 3D gait analysis is the gold standard for understanding movement as it captures movements, muscle activity and forces that the eye can’t see. We can paint an accurate picture of someone’s walking pattern by recording muscle activity, forces that are happening at the joints, and movement in 3D. When gait is affected at more than one joint level (i.e. at the knee, ankle, and hip) 3D gait analysis is the preferred method to isolate what is happening at each level.
Finally, 3D gait analysis provides us with more information to make decisions about treatment plans. This can include surgical-decision making, aiding in orthotics/prosthetics selection and can provide relevant information to develop rehabilitation plans.
3D Gait Analysis Equipment
The technology that will be used in your gait assessment will include some, or all, of the following components:
Cortex Kestrel 4200
 |  |
These cameras are responsible for tracking lower-body movement and generating the kinematic measurements explained above. Twelve of these motion capture cameras are used in combination with reflective markers in order to track your movement.
AMTI High Frequency Force Plates
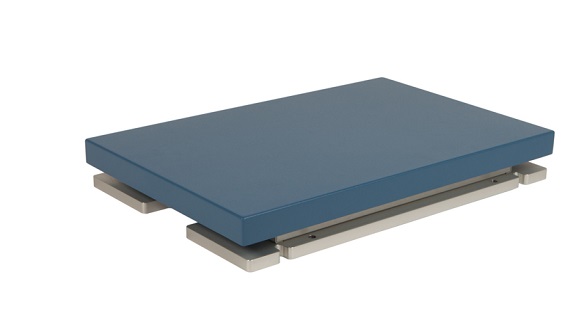
These force plates are responsible for determining the ground reaction force during walking and generating the kinetic measurements explained above. Two of these force plates are used in combination with motion tracking data in order to track joint forces and powers.
Delsys Trigno Wireless EMG
 |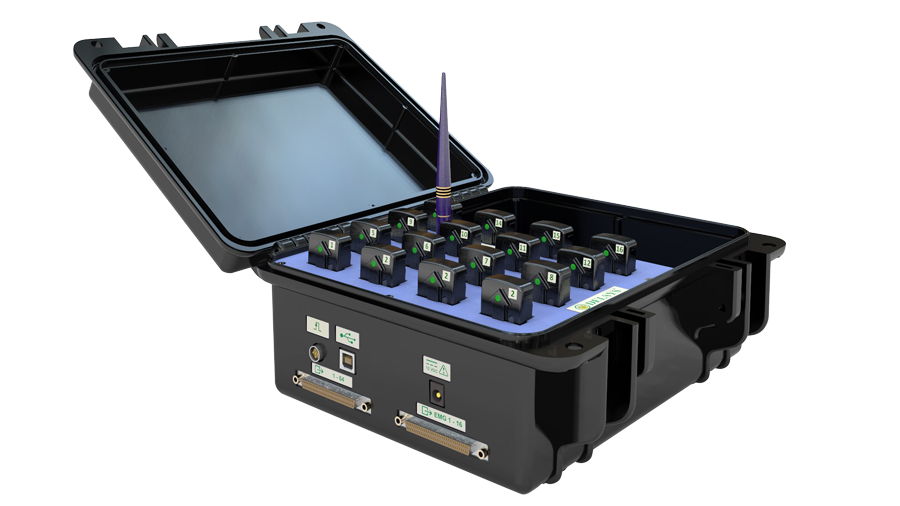  |
These units are responsible for determining the muscle activity during walking and generating the muscle activation profiles explained above. Ten of these sensors are placed at relevant locations on the lower body to understand muscle on/off patterns during gait.
